Urology
At LHWIC, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive care for patients with complex urological conditions. Our approach combines the precision of modern medicine with the restorative benefits of integrative therapies, ensuring each patient receives safe, effective, and individualized treatment.
Through our Neuro-Acupuncture framework, we address a wide range of urological concerns, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), urinary incontinence (urge, stress, and mixed types), overactive bladder (OAB), prostatitis, urological malignancies, and neurogenic bladder dysfunction. By aligning acupoint stimulation with advanced neurological insights, our treatments extend beyond symptom relief to promote long-term neural and functional recovery.
Grounded in modern neuroscience and supported by functional imaging studies, our methods are evidence-driven and outcome-focused. Every intervention is carefully tailored to enhance neuroplasticity, restore pelvic-floor function, and improve quality of life—while reducing the need for long-term medication dependency.
At LHWIC, we believe true healing happens when the body’s natural systems are respected and supported. By integrating traditional wisdom with modern innovation, we aim not only to restore physical health but also to nurture our patients’ confidence, comfort, and overall well-being.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, commonly affecting men over the age of 50. The prostate encircles the urethra; when it enlarges, it compresses the urethral lumen, leading to lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). It is frequently seen in elderly males due to hormonal changes (particularly increased activity of dihydrotestosterone. It can present as voiding and storage symptoms.
-
Voiding symptoms: hesitancy, weak stream, intermittency, straining, incomplete emptying.
-
Storage symptoms: frequency, urgency, nocturia, urgency incontinence.
-
Complications: recurrent urinary retention, recurrent infections, bladder stones, hydronephrosis, and, rarely, renal impairment.
Management of BPH involves the use of herbal medications which will inhibit the testosterone hormones (DHT) which prevents the further growth of prostate as well as herbs such as Cortex Phellodendri which will relax the bladder neck that enables more complete urination of individuals. In addition, electroacupuncture also aids in the management of storage symptoms such as frequency, urgency and nocturia. This is especially seen in patients with prostate cancer as shown in a 2025 trial published in JAMA Oncology [1].
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland which results in pain in the groin area, pain on urination or erection, cloudy urine, frequency, urgency, and blood in urine. It can be divided into 1. Acute Bacterial Prostatitis 2. Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis 3. Chronic Prostatitis 4. Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis. Risk factors include young or middle-aged adulthood, previous prostatitis, infection of the urinary or reproductive system,
HIV infection or AIDS, use of a tube inserted into the urethra to drain the bladder (urinary catheter), and diagnostic sampling of prostate tissue (biopsy). Treatment of prostatitis is dependent on whether it is a bacterial or non bacterial prostatitis.
In bacterial prostatitis, herbs with antibacterial effects are utilised. They are used to ensure that the underlying causative bacteria is being eliminated to prevent further worsening of inflammation. In the case of a non-bacterial prostatitis, the role of antibiotics or herbs with antibacterial effects can be limited. Neuroelectroacupuncture around the penile area (see 6 point acupuncture) as well as pTNS, helps with the reduction in the underlying inflammation and modulation of penile nerves to reduce the overlying symptoms such as pain, discomfort, urgency and frequency. In addition, herbs with anticholinergic effects can also be used to reduce the frequency of urination and urgency.
Overactive bladder
Overactive bladder also known as OAB refers to a frequent and sudden urge to urinate that might be difficult to delay. It occurs in 11-22% of adults in Singapore, aged 40 and above, and the incidence increases along with age. There are many different causes of it, but it can be divided into physiological, psychological, pharmacological, endocrinological and pathological.
Physiological: excessive drinking of caffeine, tea, fluids and alcohol.
Psychological: Mental health conditions such as anxiety or stress.
Pharmacological: Drugs which increases the urine output such as diuretics.
Endocrinological: Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes Insipidous
Pathological: Urinary tract infections, urinary stones, cyst and tumours.
Management of OAB requires the understanding of the underlying cause. Conservative treatment involves the reduction of coffee, tea, fluids as well as pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercise). If conservative management fails, patients be started off with herbs which help to reduce the sensitivity of the bladder, such as Sinapis Albae Semen and Stemona japonica, which have anti-cholinergic effects. [2] Medical management can also be accompanied by neuromodulation via electroacupuncture to increase the efficacy.
Neuromodulation via electroacupuncture
1. Sacral Nerve Stimulation: Sacral nerve stimulation involves the placing of needles around the lower back of the spine where the foramina (holes in the spine) are located. The sacral nerve exits from the spinal forma and supplies the urinary bladder, bowels and lower limbs. Success rate of Sacral nerve stimulation is around 75% and can be increased with the use of medications. [3]
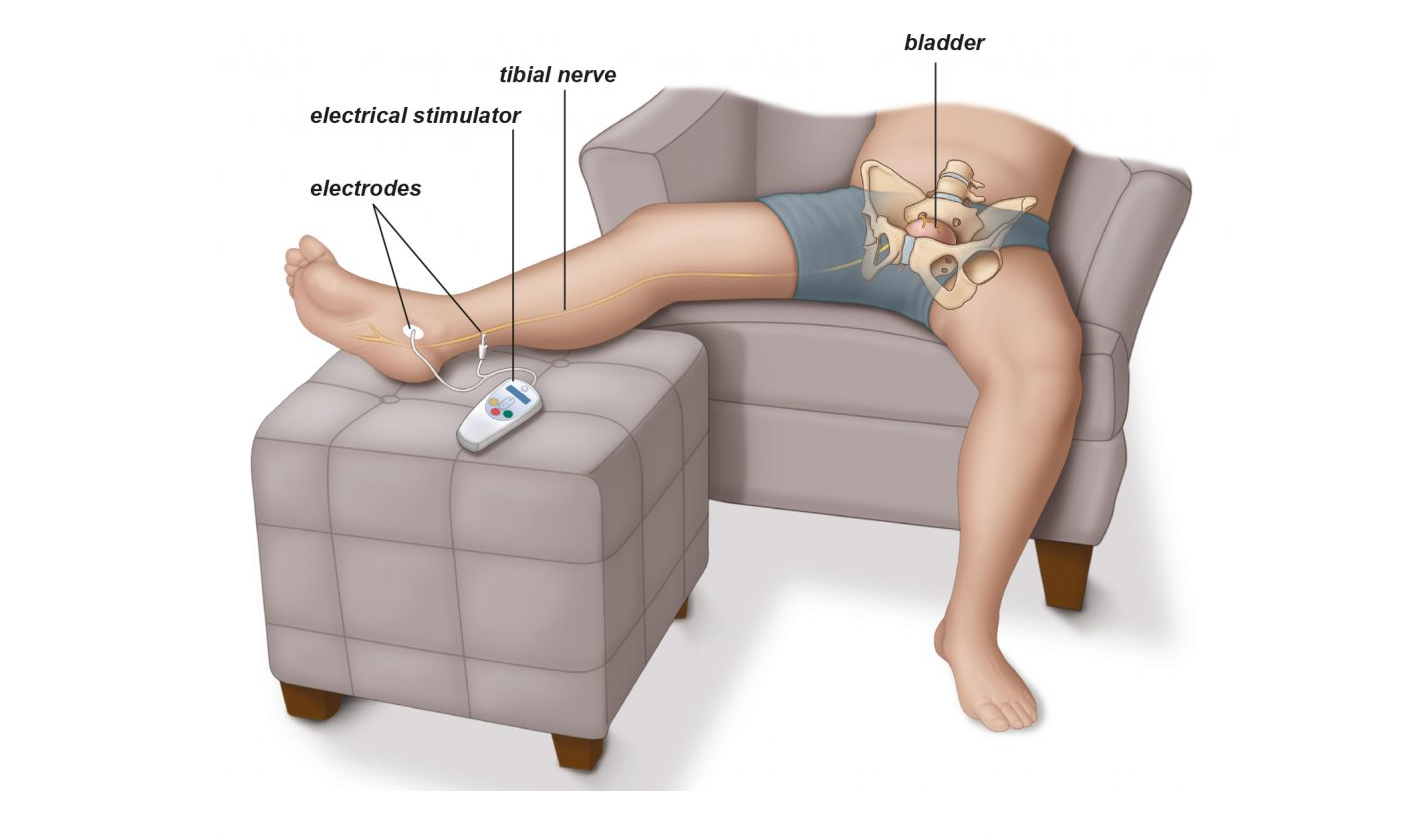
2. Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation (PTNS): involves the placing of needles around the location of sanyinjiao acupoint (see below). It is a technique that was picked up by the medical community with reference to the TCM acupoint. It is a minimally invasive procedure that has been shown to improve the symptoms of OAB. [3] The success rate ranges from 37-82% and averages around 70% for both male and females. [5]
Commonly encountered conditions
Urological diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the urinary tract (kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra) as well as the male reproductive system, including the prostate and genital organs.
Common urological conditions include:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate causing frequent urination or weak urine flow
- Prostatitis: inflammation of the prostate, often accompanied by pelvic pain and urinary symptoms
- Overactive Bladder (OAB) – sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate
- Urinary Incontinence – involuntary leakage of urine (stress, urge, or mixed types)
- Neurogenic Bladder- difficulty passing out urine, low volume or no volume (oliguria, anuria), or poor stream
- Urinary Tract Infections– bacterial

How Can Acupuncture Help?
Acupuncture has increasingly been recognized as a complementary therapy for urological disorders, especially when conventional treatments alone are not sufficient or cause side effects. By integrating Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) principles with modern neuroanatomy, acupuncture provides a holistic yet targeted approach.
1. Nerve Stimulation and Regulation
Many urological problems involve nerve dysfunction, such as weak bladder control or impaired erection.
Acupuncture stimulates peripheral and autonomic nerves (like the pudendal, ilioinguinal, or dorsal penile nerve) to restore normal nerve signaling, helping improve urinary and sexual function.
2. Improved Blood Flow
Poor circulation is often a contributing factor in erectile dysfunction and chronic pelvic conditions. Acupuncture promotes microcirculation and vascular dilation, which helps enhance oxygen and nutrient delivery to the affected tissues.
3. Pain and Inflammation Reduction
Conditions like prostatitis or interstitial cystitis are often marked by chronic pelvic pain and inflammation. Acupuncture activates the body’s natural anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving mechanisms, offering drug-free symptom relief.
4. Hormonal and Energetic Balance
From a TCM perspective, the kidney system governs urinary and reproductive health. Acupuncture helps balance the body's Qi, particularly supporting the kidney and liver meridians, which play a central role in urological function.
Clinical Applications
Modern techniques like Neuro-Electroacupuncture, as developed by physicians like Dr. Wong Lin Ho, enhance traditional methods by using electrical stimulation on precise nerve-related acupuncture points, guided by anatomical knowledge and sometimes ultrasound imaging.
- This advanced approach has shown promising results in treating:
- Overactive bladder
- Prostatitis
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Urinary retention and incontinence
What Can I Expect?
Thorough Urological examinations will be carried out together with Chinese Medicine pulse taking to identify the root cause of the issue. You will be given a diagnosis based on Western and Chinese Medical knowledge. Treatment will then be carried out coupled with traditional chinese herbal medications.
Acupuncture will be done based on different areas located within the lower abdominal regions where the bladder is located, penile region, sacral regions around the sacral nerves, as well as the pretibial nerve (pTNS).
Neuroelectroacupuncture around the penile and bladder region, as well as pTNS, helps with the reduction in the underlying inflammation and modulation of penile nerves to reduce the overlying symptoms such as pain, discomfort, urgency and frequency. In addition, herbs with anticholinergic effects can also be used to reduce the frequency of urination and urgency.
Minimally invasive procedure to cure your Urological conditions that is difficult to manage purely by medications alone and reduces the need for surgical interventions.
References
1. Liou KTCarlsson SAjay D, et al. Acupuncture for Nocturia in Survivors of Prostate Cancer: The NOCTURNAL Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2025;11(7):791–794. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2025.1199
2. Zhang M, Vrolijk M, Haenen GRMM. The Screening of Anticholinergic Accumulation by Traditional Chinese Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 21;19(1):18. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010018. PMID: 29267212; PMCID: PMC5795969.
3. Kaaki B, Gupta D (2020) Medium-term outcomes of sacral neuromodulation in patients with refractory overactive bladder: A retrospective single-institution study. PLOS ONE 15(7): e0235961. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235961
4. de Wall LL, Heesakkers JP. Effectiveness of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. Res Rep Urol. 2017 Aug 14;9:145-157. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S124981. PMID: 28861404; PMCID: PMC5565382.
5. Cristina Palmer, Bilal Farhan, Nobel Nguyen & Gamal Ghoniem (2019) Clinical outcomes of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in elderly patients with overactive bladder, Arab Journal of Urology, 17:1, 10-13, DOI: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1590032
Bringing you the best of both worlds
